Risk Management
A well-defined risk management framework is integral to any business. PEL has an independent and dedicated Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) system to identify, manage and mitigate business risks. Risk management, internal controls and assurance processes are embedded into all activities of the Company.

ENTERPRISE RISK MANAGEMENT
PEL’s ERM framework is designed by integrating the COSO* framework at its core.
The Risk Management Group (RMG) establishes the risk policy and processes for risk evaluation and measurement, whereas business units focus on developing and implementing mitigation measures, while taking controlled risks. Specific risk approaches are in place for financial and non-financial businesses.
The Company ensures seamless interaction between the Strategic Business Units (SBUs) and RMG to assess the real risks and their severity on the business. The RMG is independent of SBUs and reports directly to the Board. PEL believes in embedding a risk management culture in all facets of business decisions to ensure sustainable growth of the organisation.
The Board
The Board oversees PEL’s risk management programme. It regularly reviews and evaluates the programme to ensure adequate policies, procedures and systems are in place to execute the strategy and manage related risk. The Board-level Risk Committee reviews the macro-level risks and reports it to the Board. In FY2018, in addition to the existing Audit and Risk Committee, a new Board-level committee – Risk Management Committee for Financial Services – was formed to focus on strategy and risk management practices followed in the Financial Services business unit.
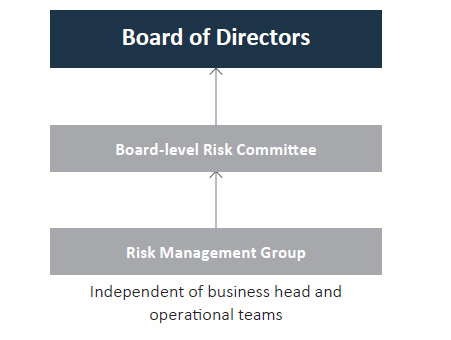
Periodically, the RMG appraises the portfolio health in the the Financial Services vertical and the risk profile of the business verticals in non-Financial Services businesses to the Board.
Business Heads and Teams
Business heads and operational teams assess the risk profile of their businesses/transactions and propose measures to mitigate the risks. They work closely with RMG to provide requisite information about the transactions or business environments and assist in creating risk registers.
*COSO - Committee of Sponsoring Organisations of the Treadway Commission
Evolution of the Risk Management Group

FINANCIAL SERVICES BUSINESS
The RMG independently assesses all investments and loans of PEL’s Financial Services business. The Group uses internal risk assessment models to evaluate credit, market and concentration risks embedded in any deal. Based on the assessment, the Group recommends a plan to mitigate or eliminate the identified risks in the investments.
Risk Assessment Approach
The approach involves identification and measurement of risk for each investment. Risks are classified into quantifiable and non-quantifiable risks.
- Quantifiable risks are estimated as the deficit in cash flow under stress testing
- Non-quantifiable risks are estimated through comprehensive scorecards and standard mark-ups
- Security value, promoter evaluation, exit options, etc. are rated through scorecards
- Operational and concentration risks are covered through standard mark-ups
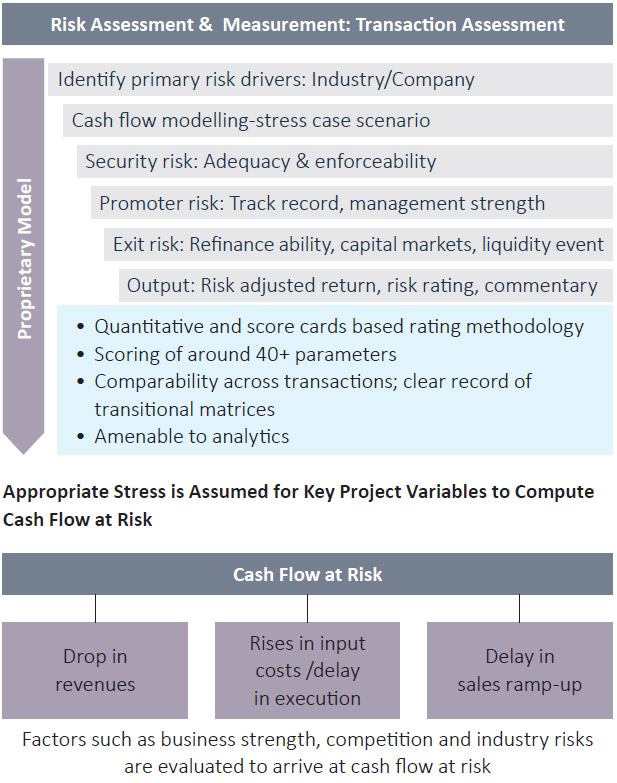
The Risk team considers various factors such as historical performance, execution capability, financial strength of the promoter and company, competitive landscape in the industry and specific segment, regulatory framework and certainty, impact of macro-economic ‘changes’, etc. while assessing the deal. The security structure is assessed for value, enforceability and liquidity. The rating generated is used for internal benchmarking and pricing. The Credit team take inputs from the RMG to arrive at optimal deal structuring.
Portfolio Revaluation Process
All executed deals are re-valued by the RMG at regular intervals. The portfolio revaluation provides the Management with the latest overview of the portfolio performance. It also triggers specific action plans for identified deals and data-based insights for enhancing underwriting criteria for future deals. The deal-specific action plans are duly executed by business teams to mitigate or eliminate the identified risks. Also, the insights are used as feedback for better credit underwriting in the future.
Stress Testing
Stress Testing is one of the key tools to assess balance sheet strength under various macro-economic scenarios. The Group has a Board-approved macro-economic Stress Testing mechanism, which has been designed internally, incorporating some of the best global practices. The Stress Testing framework covers both the assets and liabilities. The results of the stress test are discussed at the Risk Management Committee (Financial Services) of the Board.
Underwriting and Risk Mitigation
Generally a conservative, data-driven underwriting and structuring approach is adopted. The deal-related idiosyncratic risk and the risks emanating from exogenous events are thoroughly analysed as a part of the risk assessment process. The impact of any event on specific micro-markets, industries and product segments are carefully analysed and the deal underwriting criteria is altered accordingly.
Additionally, in case of non-real estate loans and investments, a detailed external due diligence is conducted. The external due diligence combined with internal understanding is assessed by Credit Underwriting and Risk teams to structure and analyse the deal. Larger deals and deals done in new sectors are presented to internal committees, which have independent experts with considerable experience.
Governance Structure
A robust governance structure for risk management process has been put in place. Various committees, both at Senior Executive Management level and at Board Sub-committee level, have been formed to evaluate the risk and risk management process at PEL
Framework to evaluate Risk Adjusted Returns
The Risk team assesses every loan proposal independently using proprietary risk assessment models
RETAIL RISK MANAGEMENT
PEL determines the creditworthiness of a borrower, based on the policy and process standards set by the Company. There are several credit checks and controls, at multiple stages of the loan process, to maintain and strengthen the asset quality of the portfolio. Following are the credit checks and controls at various stages:

Approval Process and Delegations
The sanctioning authority has been assigned based on the level of hierarchy within the organisation to ensure smooth processing of loan applications. However, at the transaction level, exceptions are built in to capture the severity of risk. Also, critical policy revisions (new product / income programmes, etc.) are jointly approved by the National Credit Manager, COO and Compliance Head and placed to the Group Risk Head and Board for ratification on quarterly basis.
Operational Risk
Operational risk is the risk of loss resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes, people and systems or from external events
To manage risk of loss resulting from Retail Operational Risk, an independent Operational Risk Management (ORM) Team is putting in place the framework and review mechanism to manage and measure the effectiveness of governance, risk management and internal controls. This framework comprises two lines of defence:
- Line Business Management (Including Support and Operations): Manages operational risk on a daily basis, maintains internal controls, designs and implements internal control-related policies and procedures
- Operational Risk Management: Develops and implements policies, procedures, tools and techniques to assess and monitor the adequacy and effectiveness of the internal controls
NON-FINANCIAL SERVICES BUSINESSES
Risk assessment at Non-Financial Services business units is carried out using risk registers. Risks across different business units and their probability, impact and mitigation plans are properly documented at regular intervals. These risks are then aggregated, and key risks across each business units along with the proposed mitigants are presented to and reviewed by the Board on a periodic basis.
Another important focus area for PEL in mitigating risks associated with the non-Financial Services business is to harness quality as a culture. The Company has a strong belief that quality is driven by a concern for patient safety. An exemplary quality framework is implemented at PEL’s facilities as well as at several contract manufacturing operations. A deep commitment to building a quality-driven organisational culture has helped PEL achieve the highest level of regulatory compliance. These have been explained in detail in the Pharma section.

MAJOR RISKS AND MITIGATING ACTIONS
The major risks perceived by PEL, along with the measures taken to mitigate them are as follows:
| Impact | Mitigating Measures |
| Default and Concentration Risk in the Financial Services Business | |
In the Financial Services business, the risk of default and non-payment by borrowers may adversely affect profitability and asset quality. The Company may also be exposed to concentration risks across sectors, counterparties and geographies. |
At PEL, each investment is assessed by the investment team as well as an independent risk team on the risk-return framework. The combined analysis of these teams is presented to the Investment Committee for investment decision. Concentration risk is partly mitigated by the concentration risk framework, which incentivises businesses to diversify portfolio across counterparties, sectors and geographies. Some of the key measures during the year to mitigate default and concentration risks in the Financial Services business are:
|
| Client and Product Concentration Risk in the Non-Financial Services Businesses | |
|
PEL’s primary businesses are based on contracts with customers. In some contracts, a large portion is transacted with a few major customers. Therefore, any set back at customers’ end may adversely affect the Company’s financials. While some particular products generate a significant portion of the Company’s overall revenue, any drop in demand for these products may adversely affect profit margins. |
PEL’s business development teams continue to actively seek to diversify its client base and products to mitigate concentration risk. For instance, in our Healthcare Insights & Analytics business, the Top 10 clients account for less than 30% of revenues, with whom we continue to have over 10-year long relationships. |
| Product and Quality Risk | |
|
PEL is expected to maintain global quality standards in manufacturing. Some of PEL’s products are directly consumed/applied by consumers. Therefore, any deviation with regards to quality compliance of products would impact consumers worldwide, and hence, adversely affect the Company’s performance. |
A dedicated Corporate Quality Assurance Group actively monitors adherence to prescribed quality standards. PEL has a strong governance and escalation mechanism. The Company’s quality management system is independent of its businesses and reports directly to the Board. PEL is on a quality advancement journey from ‘Quality for Compliance’ to ‘Quality as a Culture’, with a focus on systems, processes, technology and people. PEL has successfully cleared 33 USFDA inspections, 143 other regulatory audits and 989 customer audits, since FY2011. |
| Adverse Fluctuations in Foreign Exchange Risk | |
|
PEL has significant revenues in foreign currencies – through exports and foreign operations. Thus, the Company is exposed to risks arising out of changes in foreign exchange rates. |
The centralised treasury function aggregates the foreign exchange exposures and takes prudent measures to hedge these exposures based on prevalent macro-economic conditions. |
| Interest Rate Risk | |
|
Volatility in interest rates in PEL’s investment and treasury operations could cause the net interest income to decline. This would adversely affect profitability of the Financial Services business. |
The ALCO actively reviews the interest rate risk and ensures that interest rate gaps are maintained as per ALCO’s interest rate view. A healthy mix of fixed-and-floating assets and liabilities enables PEL to pass on any changes in borrowing costs to customers. |
| Liquidity and ALM Risk | |
|
Mismatch in the tenor of assets and liabilities in the Financial Services business could lead to liquidity risk. |
The ALCO reviews the GAP statements and formulates appropriate strategy to manage the risk. At PCHFL, we maintain a positive Gap between cumulative inflows and cumulative outflows across all maturity buckets as on March 31, 2019. The Company shifted its borrowing mix towards long-term sources of funds and reduced its CP exposure to ~`8,900 Crores as on March 31, 2019 versus ~`18,000 Crores six months ago. |
| Regulatory Risk | |
|
PEL requires certain statutory and regulatory approvals for conducting businesses. Any failure to obtain, retain or renew them in a timely manner may adversely affect operations. A change in laws or regulations made by the government or a regulatory body can increase the costs of operating a business, reduce the attractiveness of investment and/or change the competitive landscape. Also, PEL is structured through various subsidiaries across various countries in a tax-efficient manner. Regulatory changes in terms of repatriation and funding may lead to adverse financial impacts. |
The applicable regulatory framework is continuously tracked by various teams within PEL. Necessary and appropriate actions are undertaken to ensure compliance with all regulatory requirements |
| Investment Risk | |
|
PEL has equity investments in various companies in India. Like any other equity investment, these are subject to market conditions. |
The Company continues to effectively evaluate various risks involved in underlying assets, before and after making any such strategic investments. |
| Environmental Risk | |
|
PEL is committed to conserving resources as it recognises the importance of preserving the environment. Any non-adherence to our approved EHS practices and procedures may expose the Company to adverse consequences. |
The Company has adopted the 'reduce, reuse and recycle' mantra for natural resources. Several sustainability initiatives are underway in areas such as reduction of carbon footprint, water conservation and waste reuse/recycle. |